
Key factors affecting your IQF freezer capacity
2024-03-20 15:00In the fast-paced world of food production, the efficiency of your freezing process can be a major factor in your operation's overall profitability. The capacity of an Individual Quick Freezing (IQF) Freezer, which is crucial for optimizing production, depends on several key factors.
Understanding these can help in significantly improving freezing process's effectiveness, reduce costs, and increase output. Let's delve into the crucial factors influencing IQF Freezer capacity and how this knowledge can be leveraged to boost production efficiency.
Understanding Freezer Capacity
At its core, the capacity of an IQF Freezer refers to the highest volume of product that can be frozen within a single hour. This metric is vital for food producers looking to optimize their production processes. However, several factors directly impact this capacity:
· Freezing time.
· The quantity of product within the freezer.
· The performance of the refrigeration system (as an external factor, it will not be analyzed here).
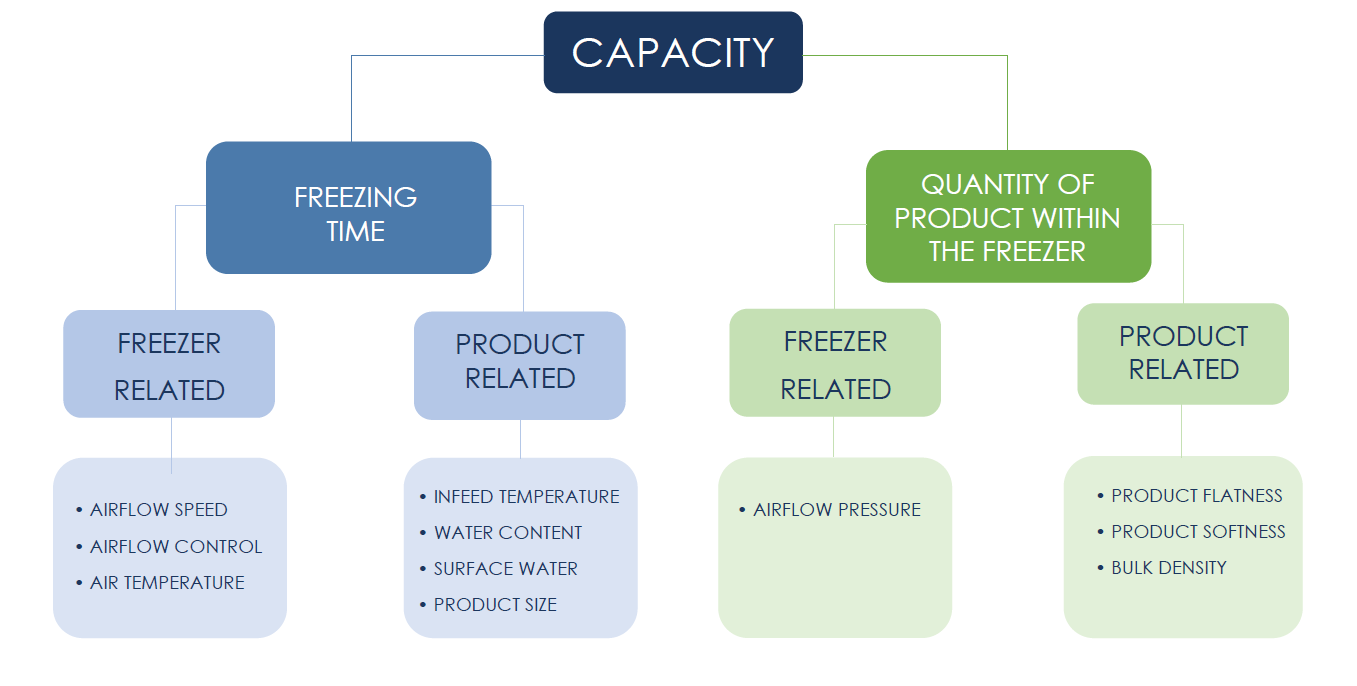
The Impact of Freezing Time and Product Quantity
The time it takes to freeze a product and the amount of product the freezer can handle simultaneously are two crucial aspects. These are influenced by a mix of freezer-related and product-related sub-factors:
FREEZER RELATED sub-factors are influencing capacity in the following ways:
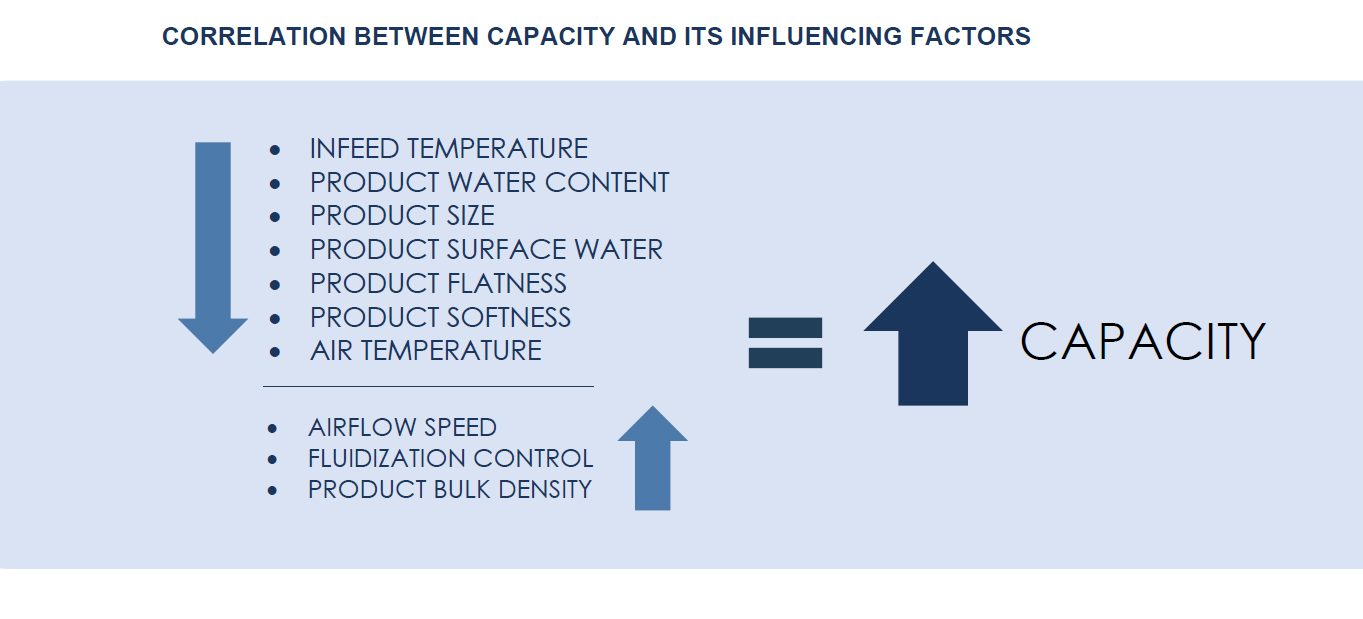
· Airflow speed: Increased airflow speed can maintain product movement even when dealing with a thicker layer of products.
· Airflow control: A higher airflow speed and high pressure drop with the help of varying hole sizes in the bedplates, generates turbulence which in turn agitates the product and allows more product on bedplate.
· Air temperature: The freezing time is shortened by a lower air temperature within the freezer; however, this factor is dependant on the efficiency of the refrigeration system.
· Airflow pressure: Increased airflow pressure enhances the fluidization of a larger quantity of product, thereby enabling higher capacity.
PRODUCT RELATED sub-factors directly influence the freezing time and quantity of product in the freezer. Consequently, capacity is affected in the following ways:
· Infeed temperature: Lowering the infeed temperature results in a shorter total freezing time, thereby increasing capacity.
· Product water content: Freezing liquid requires more energy; thus high-water content products also take longer to freeze.
· Product surface water: Reduced surface water content in the product leads to quicker freezing times.
· Product size: Heat transfer within a product core occurs at a slower rate compared to its surface, resulting in shorter freezing times and higher capacity for smaller products.
· Product flatness: Aerodynamic around a small and round product is easier compared to a flat, larger product.
· Product softness and stickiness: A sticky and soft product requires a thinner product layer and gentler treatment, which in turn results in lower freezing capacity.
· Bulk density: The weight-to-volume ratio of each product piece also impacts freezing time.
Extending Time Between Defrosts
Another aspect that significantly affects the overall efficiency of your freezing operation is the time between defrosts. This interval is primarily influenced by product surface water and infeed temperature. Minimizing surface water and lowering the infeed temperature of products can help maintain efficient airflow over the coil for longer periods, thus extending the time between necessary defrosts.
Balancing Freezing Quality with Capacity
Achieving optimal freezing quality while maximizing capacity involves a delicate balance. Factors such as product softness, infeed temperature, and surface moisture must be carefully managed. For example, a higher infeed temperature can increase freezing time and potentially compromise product quality due to the formation of larger ice crystals.
Final Thoughts
Maximizing the capacity of your IQF Freezer is a multifaceted challenge that requires attention to both the freezer's operational parameters and the preparation of the products being frozen. By understanding and optimizing the factors discussed, food producers can significantly enhance their production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and increase profitability. The key lies in a careful balance of airflow dynamics, product characteristics, and operational strategies to ensure both high quality and high capacity in the freezing process.
